Did you know that by 2025, 40% of the world’s population is predicted to have access to 5G? We were all excited about the launch of 4G, and it feels like it was yesterday. However, 5G is already on the horizon. The speed, efficiency, and capability that our mobile devices have gained in such a short period of time is astounding. 4G LTE has been the industry standard for fast internet on mobile devices, as mobile connectivity continues to develop, but 5G is rapidly becoming the next wireless technology generation. 5G is set to transform digital communications and interactions with the potential of ultra-fast speeds, reduced latency, and massive device connectivity.
This article will compare 4G LTE and 5G across various parameters such as speed, latency, coverage, cost, and applications. You will know exactly how different technologies vary and which one best meets your demands by the end.
Spis treści
ToggleCzym jest 4G LTE?
The term “4G LTE” stands for “Fourth Generation Long Term Evolution” which is a mobile network technology standard for high-speed data transfer. It is essentially the most advanced form of 4th generation mobile network technology. “LTE” is the key element, indicating the technology that makes these high speeds possible.
After data transmission, the receiver reassembles the fragmented data bits using the OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) principles. Many data packets are sent to an IPS (Internet protocol system) via LTE. It is adaptable because it incorporates MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) antenna technologies.
Key Features:
High-speed mobile internet: Theoretically, LTE’s maximum speed is 100Mbps. Practically, it tops at 15Mbps.
Wide coverage area: Typically, this provides wider total coverage, since 4G LTE uses low- to mid-frequency bands, which can go further and can penetrate structures.
Low latency for real-time applications: Low latency is ensured by the ODFMA technology supported to the LTE technology, and it reduces delays when sending big data loads.
Applications:
- Connecting different sensors and smart devices to collect and manage data.
- Voice services and other time-sensitive applications are made possible by the reduced latency.
- Users can communicate in other cities and worldwide and work remotely due to LTE.
Czym jest 5G?
5G, or “Fifth Generation of Mobile Networks” is the most recent cellular network technology standard. It offers high speeds, lower latency, and more capacity than earlier versions like 4G. This is achieved by delivering high-bandwidth data transmission for a variety of devices through the use of new radio frequencies, advanced antenna systems, and network architecture.
5G, like 4G LTE, also uses OFDM and will function using the same principles of mobile networking. To provide a greater level of flexibility and scalability, OFDM will be further improved by the new 5G NR (New Radio) air interface. Many new 5G NR air interface design strategies, including a new self-contained TDD (Time Division Duplex) subframe design, have made it possible for 5G to extend further.
Key Features:
Ultra-high speeds: 5G makes use of higher frequency bands, such as millimeter wave (mmWave), to increase the capacity of data transmission. Theoretically, the maximum speed of 5G is 20 Gbps. It is significantly faster than the maximum speed of 4G, which is 1 Gbps.
Extremely low latency: When compared to previous networks, 5G significantly reduces latency, or delay, which is essential for applications that require real-time responsiveness.
Massive device connectivity: In order to improve signal quality and capacity in congested areas, 5G makes use of “Massive MIMO” antennas. It includes multiple antenna elements that can send and receive signals to multiple devices simultaneously.
Applications:
- 5G is used in applications such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Autonomous cars, and streaming high quality HD video.
- 5G technology expands to a wide range including remote surgery, driverless cars, and improved mobile broadband usage.
Speed Comparison: 4G LTE vs. 5G
For daily use, 4G LTE offers speeds of about 100 Mbps, which is sufficient for streaming, downloading large files, and playing most online games. However, 5G technology offers significantly higher speeds. Under ideal circumstances, 5G can reach speeds of up to 20 Gbps, with 10–100 times higher speeds than 4G LTE. 5G networks continue to surpass 4G LTE even in real-world scenarios. The deployment types, low-band, mid-band, or high-band 5G determine this behavior in 5G. 5G results in these high speeds with its advanced technology, using higher frequency bands to enable better data transfer rates.

Because of these advancements, users can now download an HD movie in a matter of seconds and engage in real-time activities like online gaming and video conferencing with almost no lag. The mobile experience was revolutionized by 4G LTE, but 5G offers much more than just higher download speeds. Many new technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous cars, and smart cities, will be built on top of 5G.
Co Tesswave może zrobić dla Ciebie?
Tesswave dostarcza ponad 100 produktów antenowych i możesz skontaktować się z nami w celu uzyskania niestandardowych rozwiązań antenowych, skontaktuj się z nami już dziś, aby uzyskać bezpłatną wycenę.
Uzyskaj natychmiastową wycenę
Uzyskaj BEZPŁATNĄ wycenę, a my skontaktujemy się z Tobą w ciągu godziny
Latency and Responsiveness
The latency of 4G LTE networks is usually between 30 and 70 ms, which is low enough for most mobile applications but may still cause noticeable delays in gaming or video conferencing.
The latency of 5G can decrease to 1 millisecond. 4G LTE has higher latency compared to 5G due to its network architecture, which is less optimized for minimizing transmission delays. 5G networks are built with more efficient data handling and shorter frame intervals, reducing latency. This is perfect for mission-critical applications like remote surgery and real-time manufacturing automation.
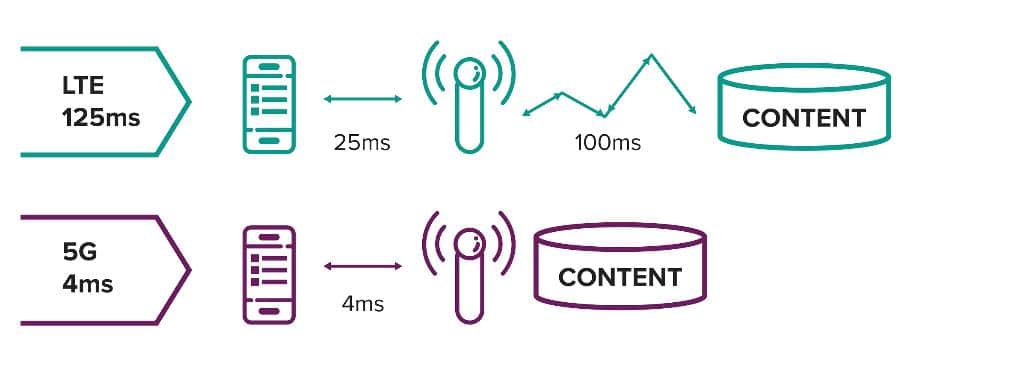
In applications where even little delays can have a big influence on the user experience, including online gaming, video conferencing, and augmented reality experiences, 5G’s lower latency translates into faster response times. Applications such as remote surgery, real-time data processing in smart cities, and driverless cars will require this near-instant responsiveness. 5G is intended to manage real-time data transmission in a manner that 4G cannot be due to its extremely low latency and huge capacity.
Coverage and Availability
Since 4G LTE uses low- to mid-frequency bands, which can go farther and penetrate structures, it often delivers wider overall coverage as compared to 5G. While 5G is designed to support many more devices, 4G LTE can manage a lot. Since these higher frequency bands are unable to pass through obstructions, 5G offers much faster speeds, especially in its high-band spectrum, while constrained to have wider coverage in some places.
With the use of technologies like massive MIMO and small cells, a 5G network can connect more than a million devices per square kilometer simultaneously. With this significant improvement over earlier mobile network generations, 5G is perfect for high-device-density settings, such as smart cities or large sporting events.
High-band 5G technology is beneficial in industries requiring high bandwidth and minimal network congestion. However, 4G LTE is a good option for coverage and consistency for operations in more dispersed or remote areas because of its capacity to get through obstacles and reach locations far away.
5G is designed to support the connected industries of the future, including automation powered by AI and robotics. 5G is the network evolution to pick if your industry is expected to grow fast and adopt cutting-edge technology.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem
4G LTE is currently the most popular mobile network technology, supported by a wide range of smartphones, tablets, and Internet of Things devices. Although currently limited, 5G-compatible devices are becoming more and more common. Because these devices use new technology, they are typically more expensive.
Smartphones and IoT devices with 5G capabilities are becoming more and more reasonably priced as 5G infrastructure grows. Compared to LTE, 5G infrastructure is more expensive and complex. For the core network to oversee network operations, new cloud-based architecture is required. Therefore, in order to construct and operate the networks, 5G will require more development and investment than LTE.
Cost and Affordability
Between 4G LTE and 5G, even though the exact price difference varies depending on the provider and location, 5G is generally more expensive than 4G LTE. It comes due to the latest technology requiring more infrastructure investment. This results in higher data plan costs for consumers, but 4G LTE is still a more cost-effective option for users who don’t need the much higher speeds that 5G offers.
- Network deployment:
5G network deployment is more costly compared to maintaining the existing 4G LTE infrastructure, which could result in higher charges for customers.
- Device cost:
5G network can also have a cost for devices that require 5G capabilities, which are usually more expensive than their 4G LTE supported devices.
- Data usage:
Although 5G delivers higher speeds, for users who may use large amounts of data, they can face a higher cost increase when they move to 5G services.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Modern 4G LTE networks use power management features to optimize energy usage, especially when in idle states, where the power consumption is significantly lower. In general, 4G LTE networks use more energy than older cellular technologies like 3G because of their faster data speeds, which require higher power levels when transferring data.
Although 5G networks are more energy-efficient than 4G, they might still use a lot of energy due to the increasing data capacity. Energy consumption also rises with mmWave transmission, edge computing, and when the applications like the Internet of Things become more common. However, the telecom sector is implementing innovation and thinking out of the box to allow the following.
- Energy-efficient cooling, chipsets, and data processing to lower baseline energy usage.
- Intelligent and dynamic management of the Core and RAN to minimize waste by reconfiguring or selectively shutting down underused resources.
- Better installation and testing procedures to find and remove inefficient causes of overlapping cell coverage, RF interference, and signal loss.
Sustainability Considerations:
5G helps with sustainability initiatives by supporting green technologies like energy-efficient automation and smart grids. Studies suggest that in terms of data bits per kilowatt, 5G networks may be up to 90% more efficient than 4G networks. Compared to 4G, this utilizes less signaling and sends data more quickly. By 2030, 5G has the potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by billions of tons.
Use Cases: When to Choose 4G LTE vs. 5G
4G LTE Use Cases:
- Mobile Broadband: Using smartphones and tablets to access the internet for purposes such as online browsing, video streaming, and data-intensive app usage.
- IoT devices in large areas: Connecting different sensors and smart devices to collect and manage data. The same LTE standard gave rise to the competing category known as NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT), which is intended for machine-to-machine use and has seen a huge rise in acceptance.
- Public Safety Networks: These provide first responders with dependable, fast voice and data connection in an emergency.
- Fixed Wireless Access: For areas where wired broadband options are limited, 4G LTE provides reliable internet connectivity.
5G Use Cases:
- High-bandwidth applications: 5G’s fast data speeds allow for the smooth streaming of big 4K video files, which demand a lot of capacity. 5G can provide feasible, high-resolution VR and AR experiences, which frequently call for 4K video streaming with a large bandwidth.
- Healthcare: Wearable technology, e-health, remote diagnostics and operations, and AI support for individuals with disabilities.
- Autonomous vehicles: In the shortest amount of time, autonomous vehicles must be able to process information and make the necessary adjustments. Fleets of autonomous vehicles will be able to get updates and make modifications thanks to the ultra-low latency, enhanced capacity, and coverage.
- Smart cities: To better serve their residents, track public utilities, and keep an eye on city infrastructure, local governments are utilizing 5G networks.
Use cases for hybrid networks: Companies may have the flexibility of 5G and LTE edge solutions in both temporary and permanent sites with no loss in safety, reliability, application performance, or management simplicity. Everything required to keep employees and important technology connected is provided by hybrid wide area network (WAN) solutions.
Wnioski
With its extensive coverage and low cost, 4G LTE continues to be the foundation of mobile connection, but 5G offers ground-breaking improvements in speed, latency, and connectivity. The decision between 4G LTE and 5G is based on availability and individual needs.
It is evident that, in the 4G LTE vs. 5G debate, each network can have its advantages. The best option for you will rely on your specific needs. Even while 5G promises far greater connectivity, reduced latency, and faster speeds, 4G LTE is still a reliable and comprehensive option for areas that don’t currently need state-of-the-art performance. The most important thing is to make sure your network is capable of meeting the demands of both the present and the future, regardless of whether you’re preparing for the transition to 5G technology or optimizing for 4G LTE.