A WiFi antenna is a device designed to transmit and receive radio waves at specific frequencies like 2.4 GHz, 5GHz, and 6 GHz. They are essential to improve signal strength and range for wireless networks. WiFi antennas are used in routers and extenders, and they play a key role by capturing and transmitting electromagnetic waves efficiently to enhance connectivity and ensure a stable and faster internet connection. WiFi antennas on routers and extenders make it possible to minimize interference and extend the reach of a wireless network. The primary purpose of a WiFi antenna in routers and extenders is to establish a seamless and reliable connection with other devices connecting to the network such as smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices. WiFi antennas are available in different shapes and sizes making it easier to integrate into other devices. Selecting a WiFi antenna for a router, a WiFi extender, or any other application depends entirely on the use case and its requirements such as range, signal strength, and the types of devices being connected. It is important to consider the gain of the antenna, the placement and orientation of it and the environmental factors such as obstructions and weather conditions when selecting a WiFi antenna for a router or extender.
Table of Contents
ToggleTypes of WiFi Antennas
Omni-directional Antennas
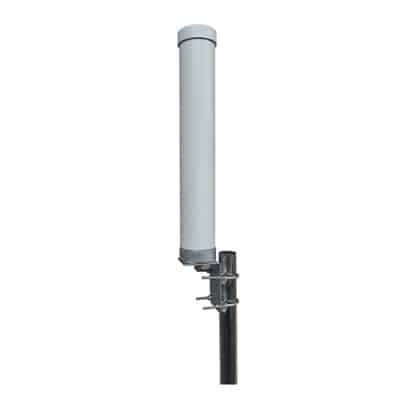
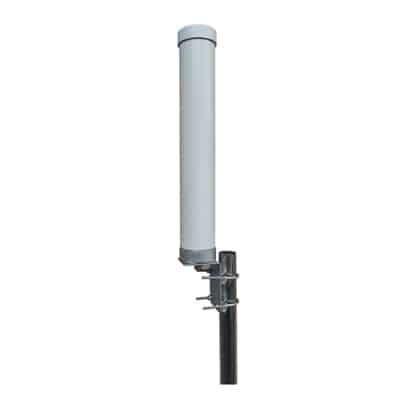
Omnidirectional antennas radiate signals in all directions equally, thus providing a 360 degrees coverage area. These antennas are typically used in home WiFi routers and access points where it is required to provide coverage spread evenly in all directions. However, since they radiate signals in all directions, the strength of the signal towards one direction and the range or distance that the signals can reach in one specific direction is limited. Omnidirectional antennas are available in various shapes and sizes from small chip antennas on PCBs to large base station antennas.
- Fiberglass omni outdoor antenna
WiFi Omni Fiberglass Antennas are antennas designed to enhance the signal strength and coverage of WiFi networks. They are manufactured using durable fiberglass materials which are weatherproof. This makes them ideal antennas to be used for outdoor applications such as parks, campuses etc. They can also be used for other applications such as marine applications, agriculture applications, industrial sites, to set up city wide WiFi networks, WiFi networks for rural and remote areas, event venues such as stadiums, convention centers, arenas etc.
- Rubber duck antenna
The WiFi Rubber Duck antenna is an omnidirectional WiFi antenna which is a flexible, rod-like antenna coated with rubber or plastic material and is generally simple, easy to install, durable and cost effective. They are widely used in applications that require users to be detected from any direction such as in IoT devices, home WiFi networks, mobile or portable applications, public wifi hotspots at locations such as libraries, cafes etc.
- Ceiling mount antenna
Ceiling mount omnidirectional WiFi antennas are easy to mount on ceilings and are generally used for distributing cellular or WiFi signals throughout a building or area. They are easy to install and typically subjected to less interference. These antennas are also used for applications such as LoRA, LTE-M, and NB-IoT. In most use cases, ceiling mount antennas are used for indoor applications.
- Whip antenna
Whip omnidirectional WiFi antennas are cylindrical in shape and are available in different operating frequencies. They are used for different applications such as WiFi integrated security cameras, IoT devices, drones etc.
- Magnetic mount antenna
WiFi magnetic antennas can be easily attached to a metallic surface to enhance the WiFi signal reception. They are small, portable, easy to install, and cost effective. They are typically used in applications such as attachments on vehicles to enhance signal reception, WiFi networks for temporary setups such as events, trade shows, or temporary workspaces, in home and office WiFi networks etc.
Directional Antennas
Directional antennas focus the signals in a specific direction, thus providing coverage to a limited area. These antennas are ideal for WiFi networks that need coverage in a particular direction. Since these antennas target all the signals in a particular direction, the signals are of high strength and hence could reach longer distances providing more range. than omnidirectional antennas. Directional antennas are commonly used in applications such as outdoor WiFi setups, point-to-point communication systems, and long-range WiFi networks. Directional antennas are available in different shapes and sizes. Few of the commonly available types of directional antennas are Yagi antennas, sector antennas, parabolic antennas, and panel antennas.
- Yagi antenna
Yagi antennas are highly directional and they generally consist of a long boom-like structure with multiple shorter elements attached on either side of it. They can be designed to operate at different frequencies by adjusting the length and spacing of the elements attached on the boom. Yagi antennas are commonly used for point-to-point connections and applications where a focused beam is needed over long distances.
- Sector antenna
Sector antennas are also another type of directional antenna that transmits or receives signals targeted towards a specific sector or area, generally found with beamwidths of 60 degrees, 90 degrees, and 120 degrees. Sector antennas are able to provide a strong signal over a specific area while minimizing interference in other directions. Sector antennas are commonly used in applications like wireless networks in campuses, by WISPs to provide coverage to specific neighborhoods, for establishing public WiFi hotspots in areas like parks and malls etc.
- Parabolic antenna
Parabolic antennas are also known as dish antennas and they work by gathering a larger amount of radio waves and focusing them into a narrow beam. Due to their high gain and high directivity, they are able to transmit high strength signals to a longer distance. They are used in WiFi networks, satellite communications, and radio telescopes.
- Panel antenna
Panel antennas are another type of directional antenna. Panel antennas can be adjusted to point in the desired direction to allow a focused beam of signals. They are often used in WiFi routers to improve WiFi coverage in specific areas such as outdoor patios, large rooms, or offices on different floors of a building. This allows the WiFi signal to be focused on a specific area, improving the strength and quality of the signal. Panel antennas are a popular choice for WiFi networks in hotels, restaurants, warehouses, and other large buildings where a strong and reliable WiFi signal is required.
The role of WiFi antenna on routers
A router is a device that connects devices at a place to the internet and directs traffic in the network to ensure that the data packets reach the desired destinations. Modern routers are generally wireless and use antennas to facilitate the signal transmission and receival between devices in the communication system. It is crucial to select a suitable antenna for the router to ensure stable and reliable connectivity. Wi-Fi antennas can play a key role in enhancing the performance of WLANs. The performance of the WiFi antenna in a router can determine the quality of the signal transmission and receival and overall decide how fast and stable the internet resources can be utilized. Besides enhancing the quality of the signals, WiFi antennas can also extend the range of your network thus allowing devices to connect from a longer distance. Also, WiFi antennas can help to reduce interference from other devices, such as microwaves or cordless phones, which can cause signal degradation.
Difference between WiFi Router, Extender and Booster
A WiFi router is a device that facilitates the connection between the devices that need to connect to the internet in a specific area and directs the traffic between the source of data and their desired destinations. Routers can be either wired or wireless.
A WiFi booster is a device that extends the range that a WiFi signal can reach. This is usually placed in between an area that has poor signal strength or no signal and the router. The WiFi booster plays the role of picking up the signal from the router, amplifying it, and then broadcasting it to the dead zones. WiFi boosters should be placed at locations where the interference of the signals from the router are minimal. A WiFi booster does not necessarily improve the speed of the connection, the download and upload speeds will remain the same. However, the quality and reliability of the network connectivity will improve with a WiFi booster. The location and the placement of a WiFi booster are crucial.
A WiFi extender is a device that can effectively reduce the distance between the connecting device and the router, thus improving the speed and performance of the WiFi network. These can ensure that high speed coverage is available throughout the desired area. A WiFi extender can be connected to a router via a wire.
Router Antenna Placement for Optimal Coverage
Identifying the best location to place a WiFi antenna for a router is extremely important. The first key factor to consider is to pick a central location. Since routers radiate signals in all directions, having the antenna in a central location will ensure that the entire signal will be radiated within the selected region unlike when placing the antenna in a corner where most of the signals will be broadcast outside. It is also important that the WiFi antenna and the router are placed as at a high and elevated position as possible. This is necessary to minimize the interferences and maximize coverage. Also, it is important to find a location that is away from other electronic devices and large metal objects as having devices in the same frequency range as the WiFi antennas will interrupt with the signals transmitted or received by the WiFi antennas on a router or extender.
External vs. Internal WiFi Antennas
External WiFi antennas are devices that are used to enhance the signal strength and range of a WiFi network by connecting it externally to routers, access points, network adapters etc., unlike the internal antennas that are built into them. External antennas can significantly improve the coverage area of a WiFi network by increasing the range in which the antenna is able to transmit or receive signals. External WiFi antennas are able to provide better signal quality strength over longer distances thus reducing dead spots. External WiFi antennas can be either directional or omnidirectional and are generally compatible with most devices. These antennas can provide enhanced range and performance, thus making them suitable for outdoor and complex environments. Another key advantage of external WiFi antennas is that they can be easily added, removed or repositioned, thus providing flexibility and upgradability. The concerns over external WiFi antennas are that they could be slightly bulky and might be slightly complex to install.
Internal WiFi antennas are antennas that are embedded into devices and they cannot be attached or detached from the device unlike in external WiFi antennas. Internal WiFi antennas are typically smaller in size and used with applications that have space limitations. Internal antennas are available in different types such as PCB antennas, chip antennas etc. These antennas are commonly used in devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, IoT devices, access points, routers, network switches etc. Key advantages of internal WiFi antennas are that they have a compact design, protected since they are housed within the device, no additional setting up is required, so it’s cost effective. However, they might have a limited range than external WiFi antennas and could be subjected to more interference. Another drawback is that it is not feasible to adjust or upgrade them. Overall, internal WiFi antennas are ideal for applications that require small and compact antennas.
Choosing between external or internal WiFi antennas for routers/extenders depends on the specific requirements both performance wise and structurally.
Key parameters of WiFi antennas
- Frequency
One of the key performance factors to consider in a WiFi antenna is its operating frequency. WiFi antennas commonly operate in the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz frequency bands. The WiFi antenna should be compatible with the operating frequency band of the WiFi router or access point.
- Gain
The gain of a WiFi antenna is a measure of its ability to focus the signals in a specific direction. WiFi antennas with higher gain can transmit and receive signals over longer distances, however, their coverage area can be limited. WiFi antennas with high gains are more resilient towards interference and hence routers with such antennas can provide connectivity for a larger number of end user devices in a selected area.
- Polarization
Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field in a signal radiated by the WiFi antenna and it is generally either vertically polarized or horizontally polarized. It is important to select an antenna that matches the polarization of the connected devices in a WiFi network to optimize the performance of the router because by matching the polarizations the electric fields of the router and the connecting devices can be aligned, thus maximizing the signal strength and minimizing interferences.
- Beamwidth
Beamwidth is a measure of the angle at which the WiFi antenna radiates or receives the signal and it determines how wide or narrow the antenna’s signal is spread. If the beamwidth is narrow, it generally means that the signal is concentrated to a smaller area and hence the strength of the signal is higher, and hence the signal can be radiated over longer distances. If the bandwidth is higher, the router will be able to transmit or receive signals in a wider coverage area, but the signal strength and the range can be lower. Narrow beamwidth antennas are ideal for point to point applications while wide beamwidth antennas on routers are better for applications that require large coverage areas.
- Connectors
WiFi antennas can be connected to routers or other devices using different types of connectors. Some of the commonly used types of connectors are RP-SMA, SMA, or N-type connectors. When selecting a connector for the antenna, it is crucial to match the impedance between the connectors, routers and the connecting devices. Cables and connectors play a significant role in minimizing interference and enhancing the overall performance of the router.
MIMO and Beamforming
WiFi antennas can be set up in MIMO (Multiple-Input,Multiple-Output) configuration. With the availability of multiple antennas linked together and oriented in different directions, a reliable and efficient WiFi network can be ensured. It can improve the data transmission rates, reliability, and stability of the network as well as the signal robustness.
WiFi antennas that are beamforming can boost the WiFi signals by directing them to certain devices or areas. Basically, the signals are directed to form a beam using multiple elements and algorithms. Thus, due to the focused radiation, it enhances the signal strength and minimizes the interference. The orientation can be changed to adjust the focused direction and ensure optimal performance and coverage.
Latest WiFi 6 & 6E technology on router and its antennas
Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E are the latest Wi-Fi technologies. The performance of the 6 GHz band is significantly better than the 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band in terms of providing faster speeds, better bandwidth, higher efficiency and higher reliability in a WiFi network. New concepts such as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), Target Wake Time (TWT), and Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) are introduced and active with the latest WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E technologies. Using WiFi antennas in routers for WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E networks will enable coverage to a larger area and to provide a seamless next generation network experience to a massive number of users providing bandwidth to support different applications and services. WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E antennas have an extended frequency range, thus providing access to more communication channels, less obstructions and better data transmission making them ideal for large range and high density environments. Routers in WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E networks use WiFi antennas and they are used in various applications such as in IoT applications in smart homes, to establish enterprise networks, for setting up public WiFi hotspots, time critical applications in healthcare facilities, AR /VR applications etc.
WiFi technology will keep improving as the requirement for internet connectivity increases day by day. Consumers expect the speed, capacity and reliability of the network to significantly improve as the WiFi technology evolves. Routers and antennas operating with WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E technology will have improved performance over the traditional 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Choosing the Right Antenna for Your Needs
When selecting a WiFi antenna for a WiFi router or an extender multiple factors need to be considered. The first and most crucial factor to consider is the performance requirements of the application. Depending on the expected data transmission rates, coverage area and the radiation distance of signals, an antenna with a suitable gain, beamwidth and operating frequency must be chosen wisely. It is also necessary to consider the obstructions and interference in the transmission path as it might degrade a signal from a router. Ability to withstand harsh weather conditions needs to be considered if the WiFi network is to be established outdoors and WiFi antennas that are weather resistant would be ideal for routers that are installed in such setups. It is also important to consider the location and the orientation of the antenna as this can have an impact on the overall performance of the antenna and the router. The antenna needs to be mounted properly and securely using proper connectors and cables with matching impedances. Another key factor to consider is the physical specifications of the antenna and the router such as the size and the design which can vary for different types of WiFi antennas. When selecting a WiFi antenna for a router it is also necessary to take into consideration other factors like the ease of installment, ease of maintenance and the initial and maintenance cost. These are just a few factors to consider when selecting the right antenna for an application and it depends entirely on that specific use case.
How to connect a WiFi antenna to router
When connecting a WiFi antenna to a router, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure that proper connection is established. If antenna connectors are not provided, it is crucial that a suitable connector that matches the impedances are chosen in order to optimize the performance of the antenna and the router. The WiFi antennas must be securely attached to the router and oriented in the desired direction such that it remains stable in that fixed orientation. Overall, it is important to clearly follow the manufacturer’s recommendations to achieve the best performance of the antenna and the router.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article discussed the use of WiFi antennas in routers/extenders. Wifi antennas are basically devices that are used to transmit and receive signals in a few common frequency bands like 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz. Routers are devices that enable the connection to the internet and direct traffic between sources and destinations. The article provides a comprehensive overview of WiFi antennas and their application in routers discussing the different types of antennas available, the performance parameters to consider, other key factors to consider when selecting an antenna, etc.